How To Increase Return On Equity
Return on Disinterestedness (ROE)
The cyberspace income of a visitor relative to the value of its equity
What is Return on Disinterestedness (ROE)?
Render on Equity (ROE) is the measure of a visitor's annual render (net income) divided by the value of its total shareholders' disinterestedness, expressed as a percentage (e.one thousand., 12%). Alternatively, ROE tin can likewise exist derived by dividing the firm's dividend growth rate by its earnings retention rate (1 – dividend payout ratio).
Return on Equity is a two-part ratio in its derivation because it brings together the income statement and the remainder sheet, where net income or profit is compared to the shareholders' equity. The number represents the total return on equity capital letter and shows the firm's ability to plough disinterestedness investments into profits. To put it another mode, it measures the profits made for each dollar from shareholders' equity.
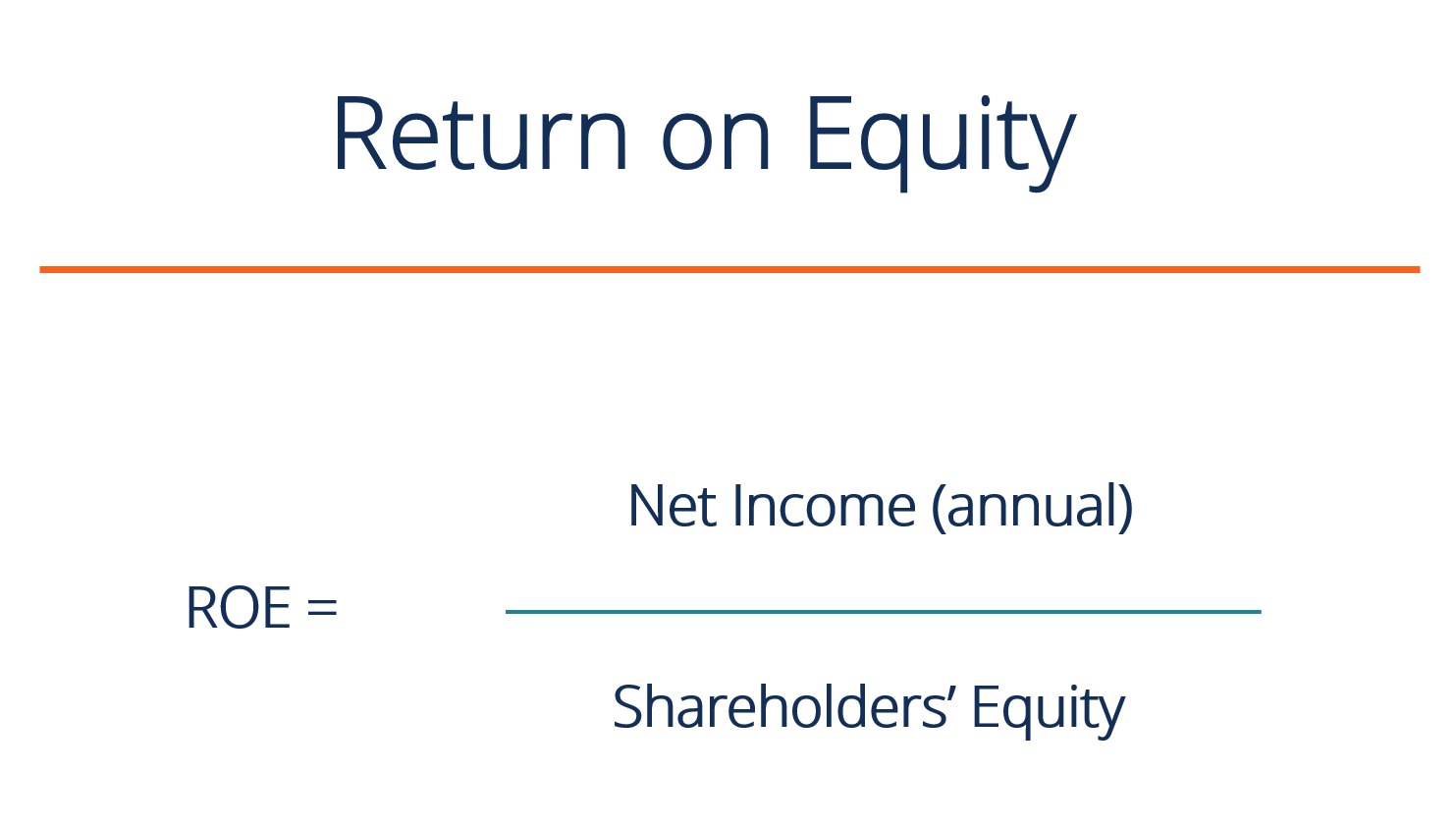
Render on Equity Formula
The following is the ROE equation:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders' Equity
ROE provides a simple metric for evaluating investment returns. By comparison a company's ROE to the industry's average, something may be pinpointed well-nigh the visitor's competitive advantage. ROE may also provide insight into how the company management is using financing from disinterestedness to grow the business.
A sustainable and increasing ROE over time can mean a company is proficient at generating shareholder value because information technology knows how to reinvest its earnings wisely, so as to increase productivity and profits. In contrast, a declining ROE tin can mean that direction is making poor decisions on reinvesting capital in unproductive assets.
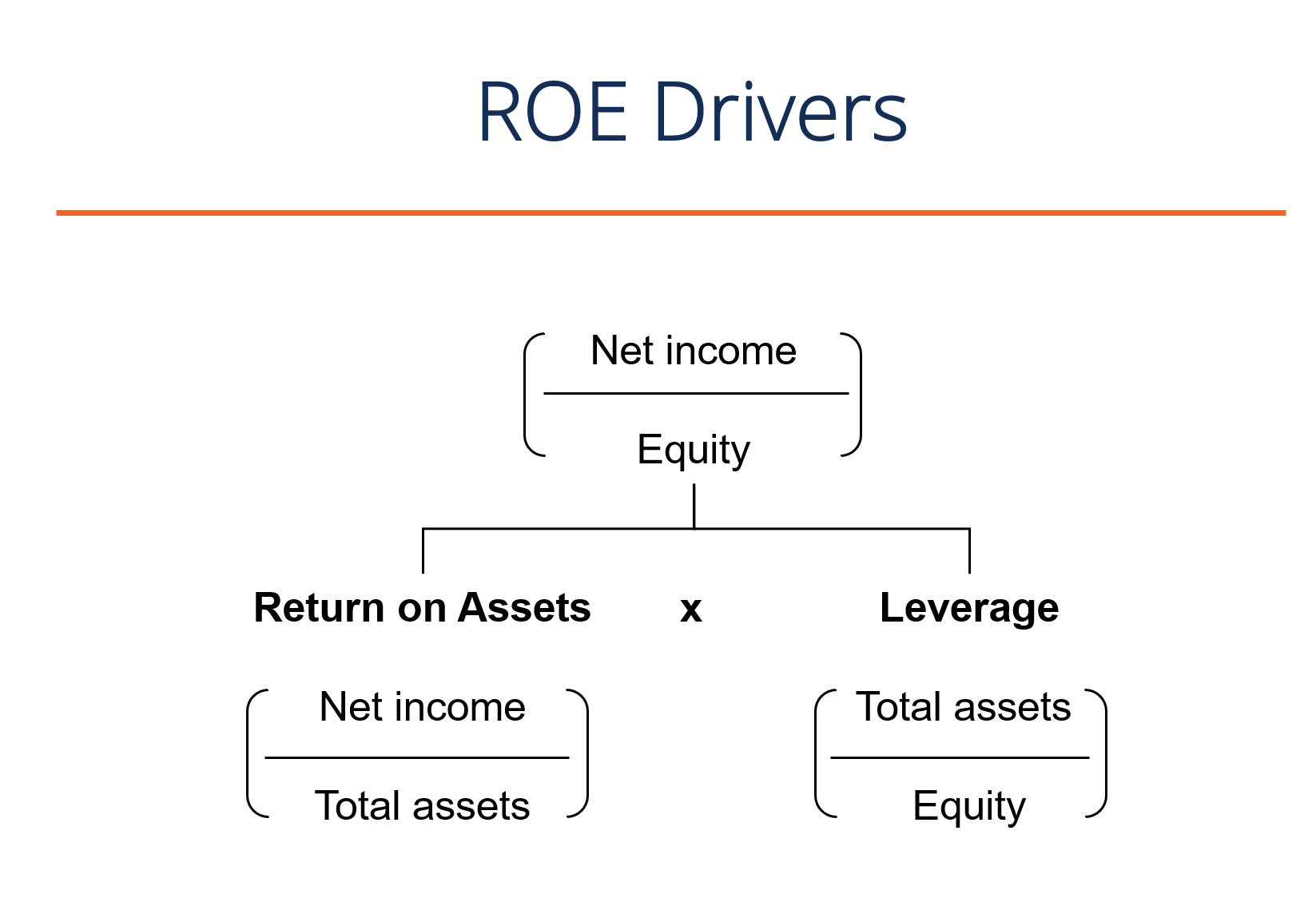
ROE Formula Drivers
While the simple return on equity formula is net income divided past shareholder's equity, we can break it downwards further into additional drivers. Every bit yous can see in the diagram below, the return on disinterestedness formula is also a function of a firm's render on assets (ROA) and the amount of financial leverage it has. Both of these concepts will be discussed in more detail beneath.
Larn more in CFI'due south Fiscal Analysis Fundamentals Form.
Download the Free Template
Enter your proper name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
Return on Equity Template
Download the gratis Excel template now to accelerate your finance knowledge!
Why is ROE Important?
With internet income in the numerator, Return on Equity (ROE) looks at the house's bottom line to gauge overall profitability for the firm's owners and investors. Stockholders are at the bottom of the pecking lodge of a business firm'due south capital structure, and the income returned to them is a useful measure that represents excess profits that remain after paying mandatory obligations and reinvesting in the business.
Why Use the Return on Disinterestedness Metric?
Only put, with ROE, investors can run into if they're getting a good return on their money, while a company can evaluate how efficiently they're utilizing the firm'southward equity. ROE must be compared to the historical ROE of the company and to the industry'due south ROE boilerplate – information technology means niggling if just looked at in isolation. Other financial ratios can be looked at to get a more consummate and informed motion-picture show of the visitor for evaluation purposes.
In guild to satisfy investors, a company should be able to generate a college ROE than the return available from a lower risk investment.
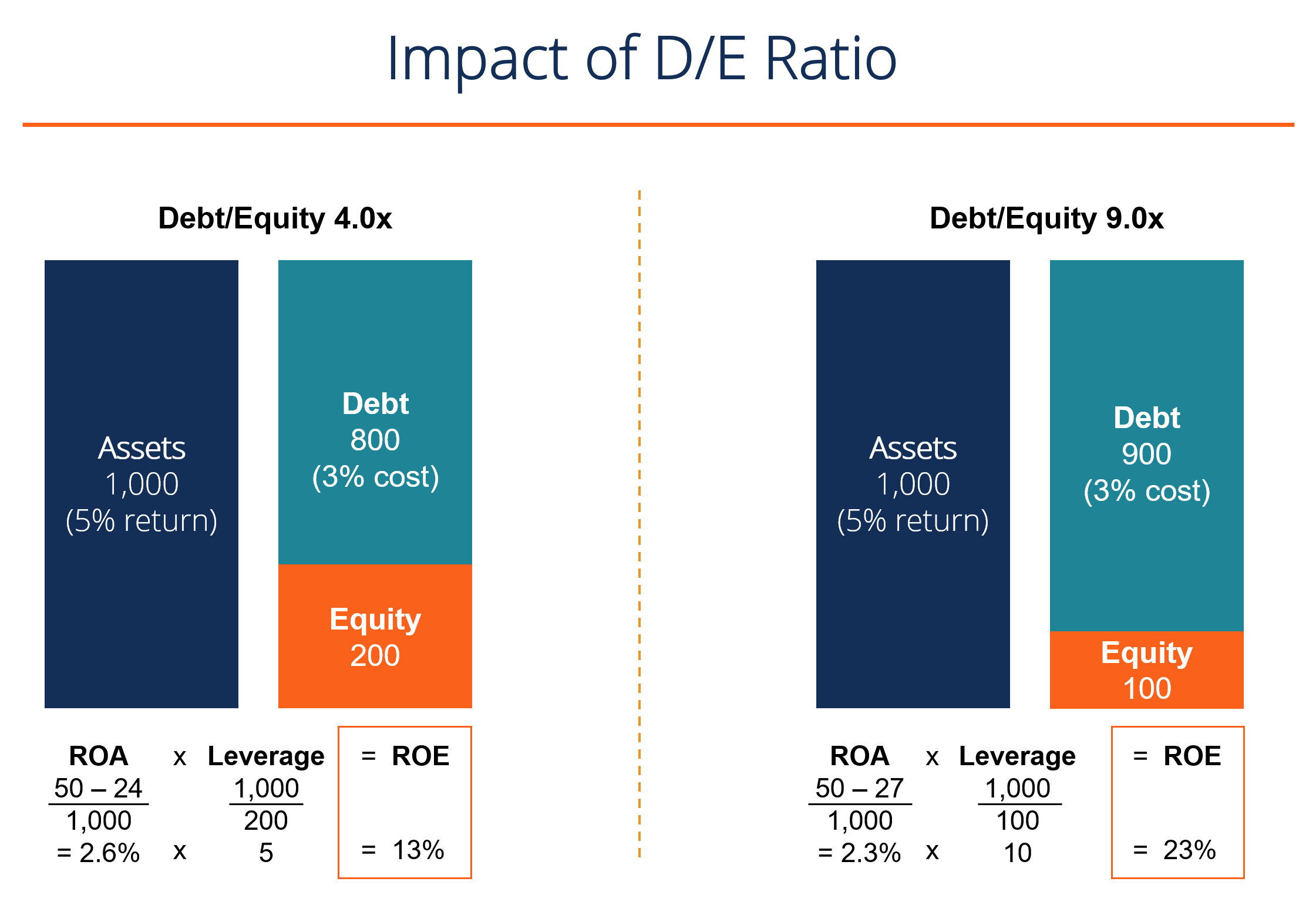
Outcome of Leverage
A loftier ROE could hateful a company is more than successful in generating profit internally. However, information technology doesn't fully show the risk associated with that return. A visitor may rely heavily on debt to generate a higher cyberspace profit, thereby boosting the ROE college.
As an example, if a company has $150,000 in equity and $850,000 in debt, then the total majuscule employed is $1,000,000. This is the same number of full assets employed. At v%, it will cost $42,000 to service that debt, annually.
If the company manages to increase its profits before interest to a 12% return on capital letter employed (ROCE), the remaining profit later paying the involvement is $78,000, which volition increment equity by more than 50%, assuming the profit generated gets reinvested dorsum. Equally we tin can encounter, the effect of debt is to magnify the render on equity.
The prototype beneath from CFI's Fiscal Assay Course shows how leverage increases equity returns.
Learn more in CFI's Fiscal Analysis Fundamentals Class.
Drawbacks of ROE
The return on equity ratio can besides exist skewed past share buybacks. When direction repurchases its shares from the marketplace, this reduces the number of outstanding shares. Thus, ROE increases equally the denominator shrinks.
Some other weakness is that some ROE ratios may exclude intangible assets from shareholders' equity. Intangible avails are non-monetary items such as goodwill, trademarks, copyrights, and patents. This can make calculations misleading and difficult to compare to other firms that take chosen to include intangible assets.
Finally, the ratio includes some variations on its composition, and there may exist some disagreements between analysts. For case, the shareholders' equity tin can either exist the beginning number, catastrophe number, or the average of the ii, while Cyberspace Income may be substituted for EBITDA and EBIT, and can be adapted or not for non-recurring items.
How to Employ Return on Equity
Some industries tend to reach college ROEs than others, and therefore, ROE is well-nigh useful when comparing companies inside the same industry. Cyclical industries tend to generate college ROEs than defensive industries, which is due to the different take a chance characteristics attributable to them. A riskier firm will have a higher cost of capital letter and a higher cost of equity.
Furthermore, information technology is useful to compare a firm's ROE to its cost of equity. A firm that has earned a return on equity college than its cost of disinterestedness has added value. The stock of a firm with a twenty% ROE will generally toll twice equally much as i with a 10% ROE (all else being equal).
The DuPont Formula
The DuPont formula breaks down ROE into three key components, all of which are helpful when thinking near a firm'due south profitability. ROE is equal to the production of a firm's net profit margin, asset turnover, and financial leverage:

If the internet profit margin increases over fourth dimension, then the house is managing its operating and fiscal expenses well and the ROE should also increase over fourth dimension. If the nugget turnover increases, the firm is utilizing its assets efficiently, generating more than sales per dollar of assets endemic.
Lastly, if the business firm's financial leverage increases, the house tin can deploy the debt capital to magnify returns. DuPont analysis is covered in detail in CFI'due south Financial Analysis Fundamentals Course.
Video Explanation of Return on Equity
Below is a video explanation of the diverse drivers that contribute to a firm'southward return on equity. Learn how the formula works in this brusk tutorial, or bank check out the full Financial Analysis Course!
Caveats of Return on Equity
While debt financing can be used to boost ROE, information technology is of import to keep in mind that overleveraging has a negative impact in the class of high interest payments and increased hazard of default. The market may demand a college toll of equity, putting pressure on the firm's valuation. While debt typically carries a lower cost than equity and offers the benefit of taxation shields, the near value is created when a firm finds its optimal capital structure that balances the risks and rewards of financial leverage.
Furthermore, it is important to keep in mind that ROE is a ratio, and the house can take deportment such as asset write-downs and share repurchases to artificially heave ROE by decreasing total shareholders' equity (the denominator).
Additional Resource
This has been CFI'south guide to return on disinterestedness, the return on equity formula, and the pros and cons of this financial metric. To keep learning and expanding your financial analyst skills, see these additional valuable CFI resources:
- Render on Assets (ROA)
- Guide to EBITDA
- Cash Flow Guide
- Financial Modeling Best Practices
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/what-is-return-on-equity-roe/

0 Response to "How To Increase Return On Equity"
Post a Comment